The European Union (EU) Artificial Intelligence (AI) Act, in force since August 2024, is an innovative and world-first regulation that seeks to regulate the development and use of artificial intelligence in the European Economic Area (EEA). Designed to respond to the ethical, social, and technological challenges posed by this emerging technology, the law establishes a comprehensive regulatory framework that prioritizes safety, ethics, and responsible innovation. Through a combination of restrictions, incentives, and oversight measures, this legislation positions Europe as a leader in the development of safe and trustworthy AI technologies.
Main Objectives of the Law
The fundamental purpose of this regulation is twofold:
- Protecting the fundamental rights of European citizens, ensuring that AI is used safely and ethically, minimizing risks such as discrimination, invasion of privacy, or algorithmic bias.
- Promote responsible innovation, establishing a clear regulatory environment that incentivizes EU technological leadership in a highly competitive global market.
Scope of Application
The law covers all AI systems developed, distributed, or used in Europe, regardless of whether they originate locally or internationally. This means that even foreign companies will have to comply with European standards if their products affect EU citizens. The legislation regulates a wide variety of AI applications, from software in public services to advanced generative tools such as chatbots.
Classification of AI Systems
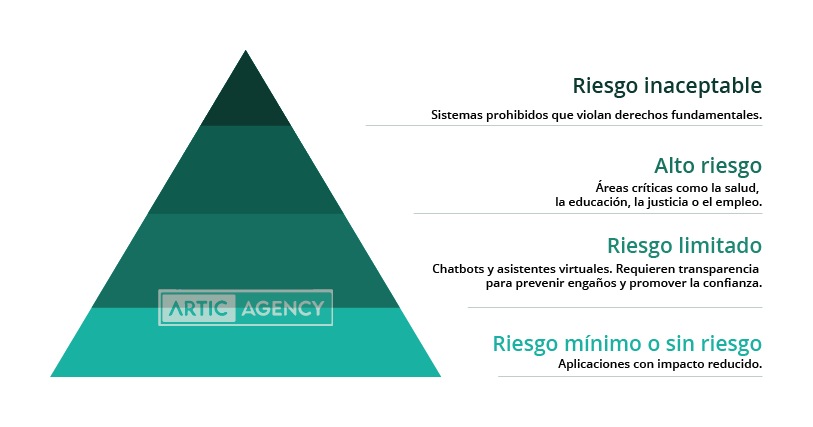
The regulations classify AI systems into four categories based on their risk level:
- Unacceptable risk: Includes prohibited systems that violate fundamental rights, such as those that manipulate human behavior without consent, tools of mass surveillance, or technologies used for widespread social scoring like China's social credit system.
- High riskTechnologies that impact critical areas such as health, education, justice, and employment fall into this category. These systems are subject to strict transparency, risk assessment, and human oversight requirements.
- Limited riskThese technologies, such as chatbots and virtual assistants, must ensure that users are informed that they are interacting with an AI. They require transparency to prevent deception and promote trust.
- Minimal or no risk: Includes applications with reduced impact, such as spam filters, writing assistants, or content recommendation systems. Although less regulated, they must comply with basic security and accountability principles.
Responsible and Ethical Innovation
The law also places a strong emphasis on ethics and transparency. It seeks to ensure that AI technologies are inclusive, accessible, and free of bias, avoiding the perpetuation of stereotypes or prejudices through the data used in their development. Furthermore, it introduces the regulatory sandbox, a safe and supervised space where companies can experiment with emerging technologies without risk of violating regulations, thus fostering creativity and innovation.
Sanctions and Compliance
To ensure compliance, the regulations establish significant sanctions, including fines of up to 61% of a company's global annual turnover or €30 million, depending on the violation. It also includes non-financial measures, such as product recalls, suspension of activities, and publication of non-compliance, which can damage the reputation of offending companies.
National Supervisory Authorities, together with the European Commission, are responsible for implementing and supervising regulations. These entities play a crucial role in risk assessment, system inspection, and promoting compliance with legal standards.
Global Impact
The scope of this legislation transcends European borders, as it applies to any technology that interacts with EU citizens. This means that companies around the world must align with European standards, promoting a global impact on the way AI is developed and used.
A Regulation for the Future
The EU Artificial Intelligence Act represents a bold step toward a safer, fairer, and more ethical digital future. By establishing clear and predictable rules, it not only protects European citizens but also incentivizes companies to develop leading technologies that meet high standards of quality and ethics. In a world where AI is rapidly transforming every sector, from healthcare to transportation, this legislation serves as a global model for balancing technological progress with social responsibility.

